San Francisco brand video production – Four day shoot for Cepton
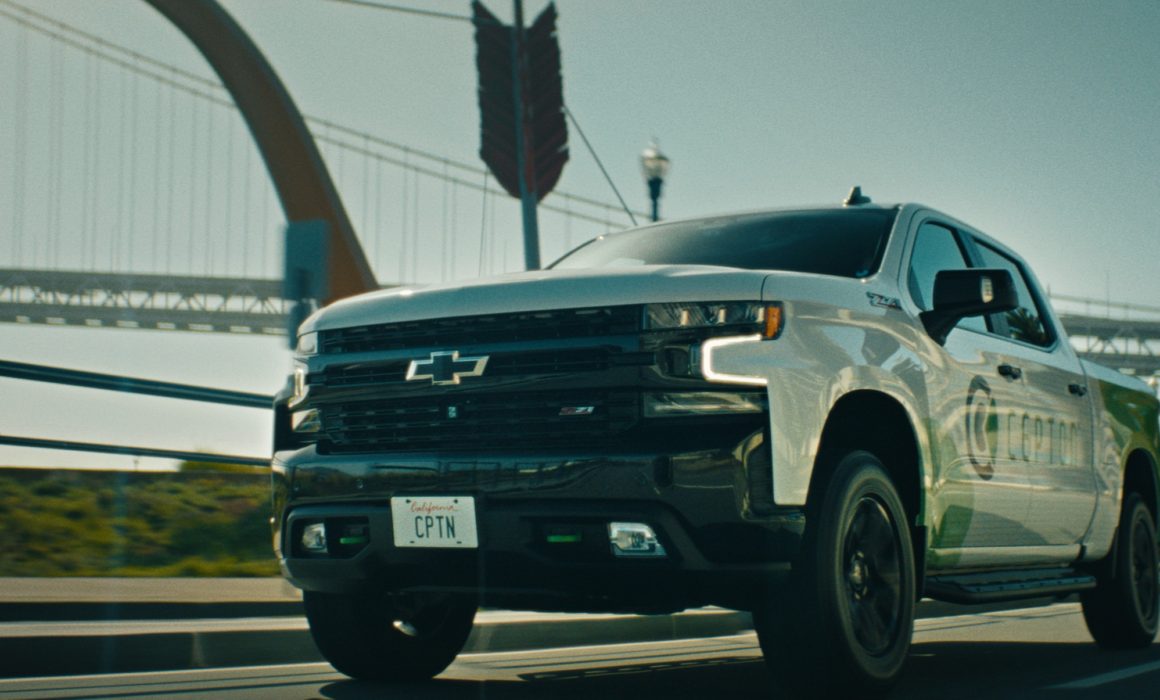
We just finished our biggest project yet! Cepton makes LiDAR for several sectors but their primary focus is automotive. We have done several small video productions for them in the past, but now that they are officially listed on the NASDAQ they felt it was time to step it up a notch. They came to us looking to make a high end brand video on a tight timeline. Our concept was ambitious. Three storylines plus an arm car day shot over four days. The goal of this video was to not only educate users about their lidar technology but to inspire viewers to understand the larger goal of the company. To bring Lidar to the masses. In this article we’ll break down how we accomplished this San Francisco brand video production. Take a look at the video below and then read on to see our process.
Approach
Our approach for this San Francisco brand video production started with a treatment. In this treatment we presented two potential storylines to the company as well as the look and feel we would be creating. It turned out that the client actually wanted to blend the lines between both of our storylines. Not a problem. We tweaked and then started with our script creation. At this point, we brought in our script writer and got to work hashing out all the details of the story. We knew that because there would be such a large lift with the pre-production in order to capture the content necessary, we wanted to be 100% locked with the script before moving on!
Our script ended up being approximately six pages. It was our guide going into pre-production!

Once the script was ready, we presented it to the client for final story sign off. We tweaked and tweaked some more and then we locked the script. At this point, the base narrative was locked and we were able to start with the pre production. The first thing we did was break down the script into a shot list. Then our producer did a full script breakdown. At this point, we knew this was going to be tricky. Four days for this concept was very ambitious! Guess we just love a good challenge.
Pre Production
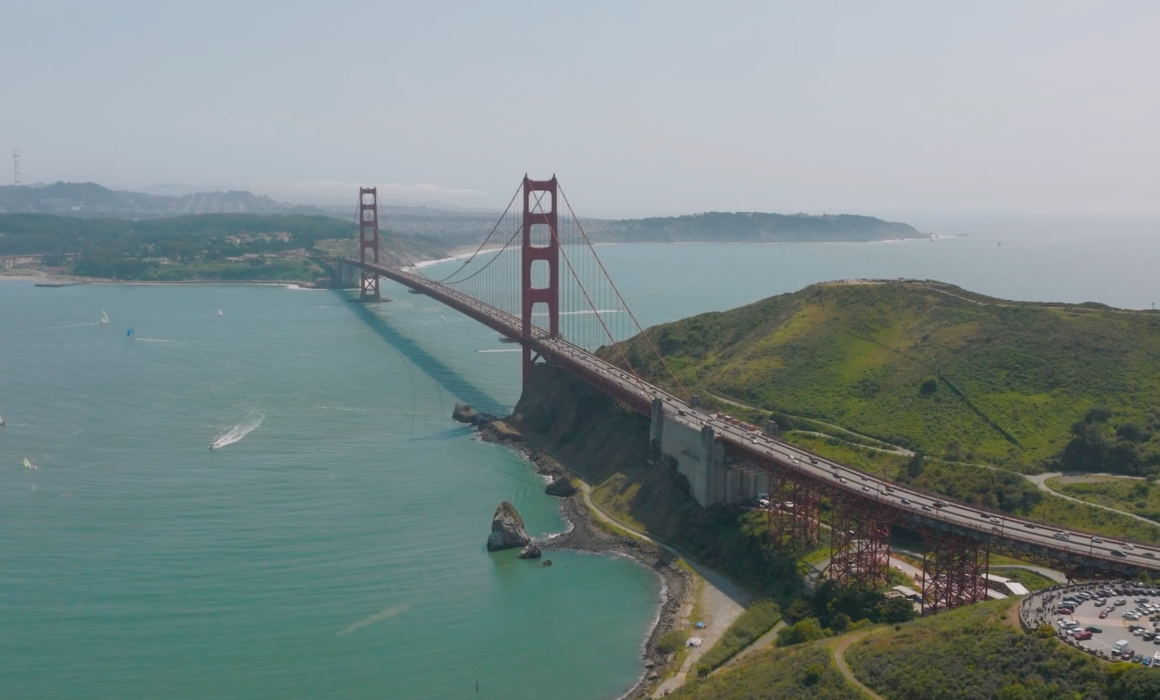
The first thing we did during pre-production was location scouting. This would be where we picked the houses and main locations for our shoot. The client loved that we were looking for distinctly different locations. They also loved the idea of shooting in San Francisco; however, this presents many logistical and security concerns. We’ve shot here many a time, but exteriors in San Francisco definitely pose a challenge. After scouting, we also decided that shooting on the highway between Muir beach and Stinson beach would be our best opportunity for some epic coastal footage. At this point, we brought on a locations manager. They helped us file appropriate permits with the city of San Francisco, state of California as well as the State Parks. This was a first for us working with so many jurisdictions.
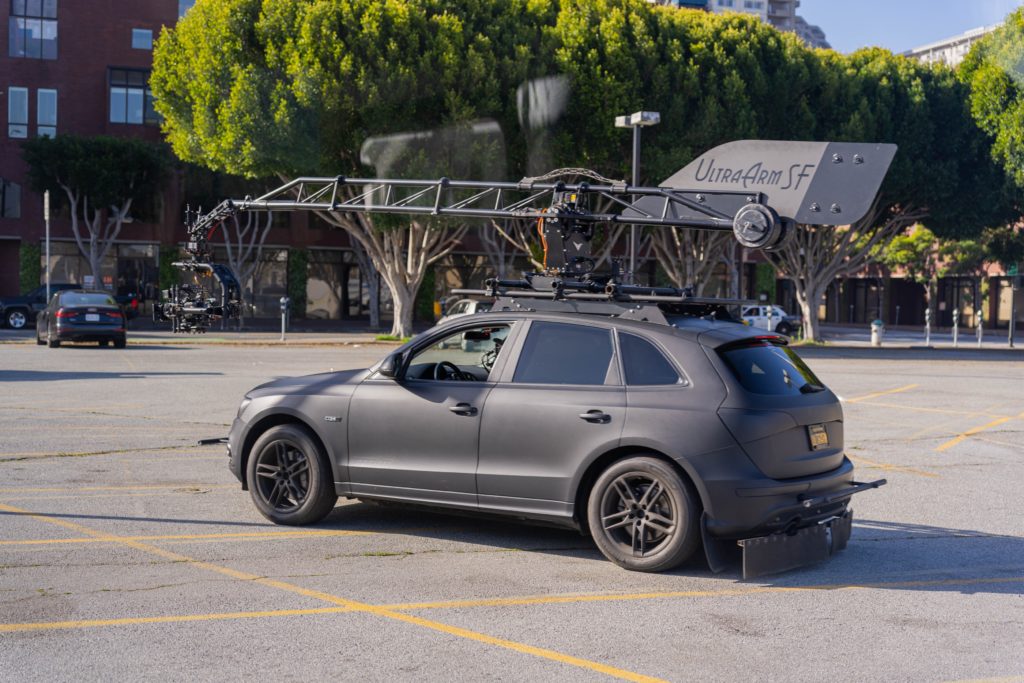
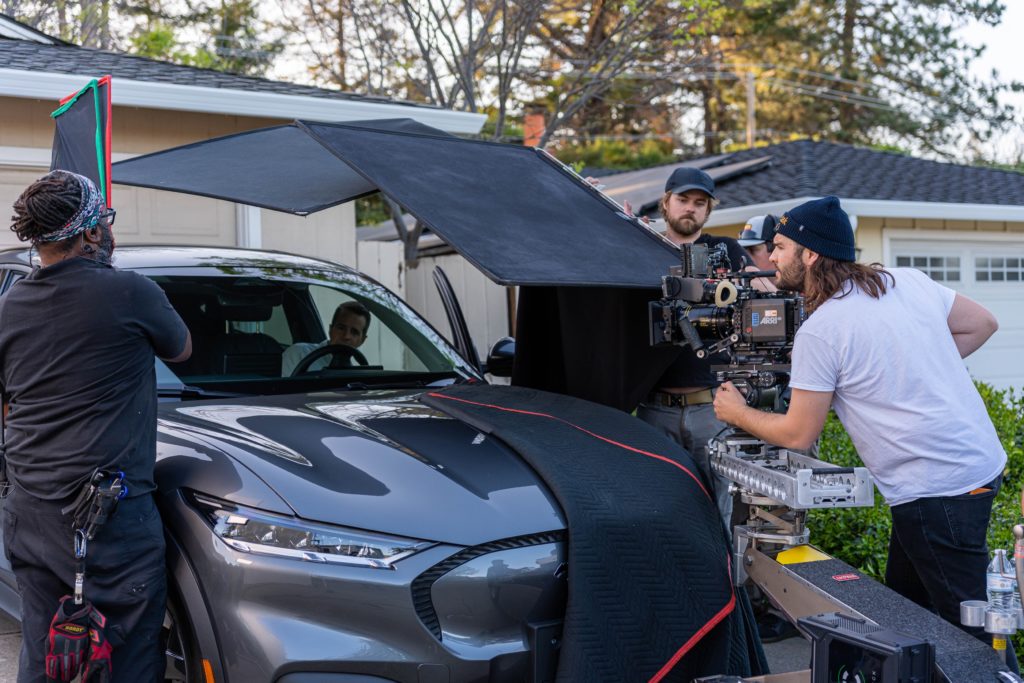
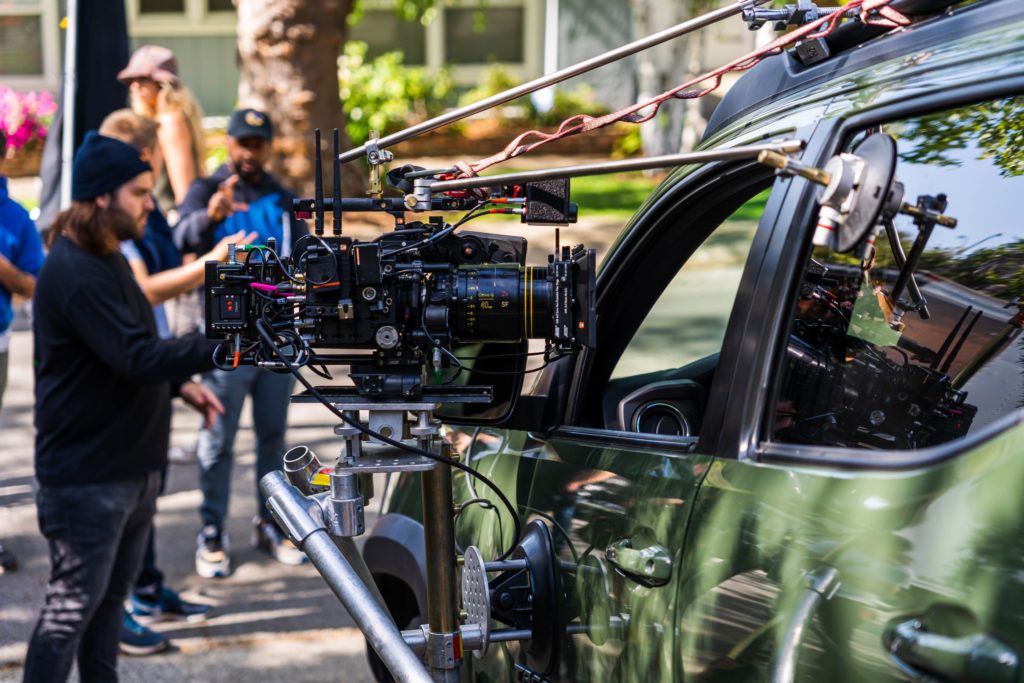
During pre-production we also began casting for our actors and picking our picture vehicles. This posed another challenge as their self driving technology wasn’t actually in any of the cars we were shooting with! The vehicles also had to be newer than 2021. After finding our vehicles we began to lock our department heads. We chose to work with a Director of photography who had experience working with cars and had completed a successful project with in the past. We also knew that a limiting factor of the production would be the availability of our arm car team. At this point, we had the core team assembled and decided to lock shoot dates.
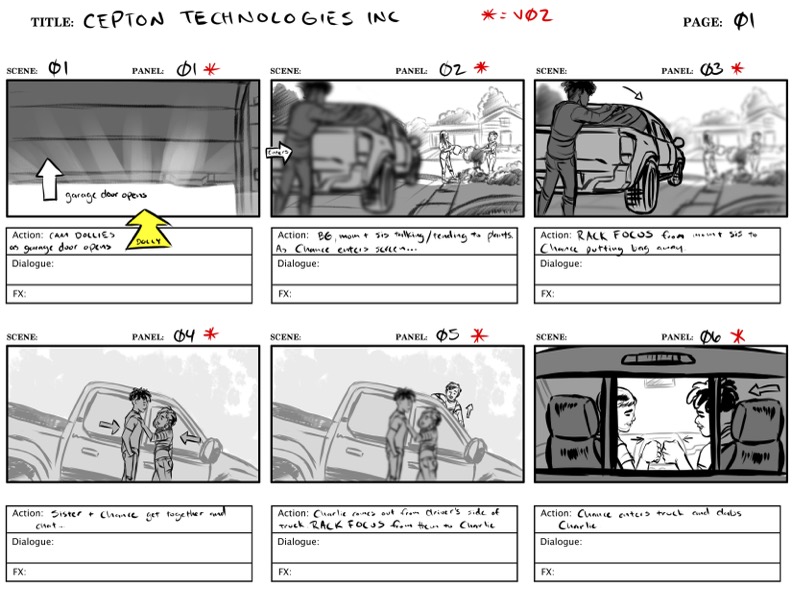
As pre-production continued, we began to storyboard. This part of the process is awesome! Everything starts to get visual and we now have a tangible communication tool with the client and all of our collaborators. Once those were locked we did our final tech scout with the crew and got ready to shoot.
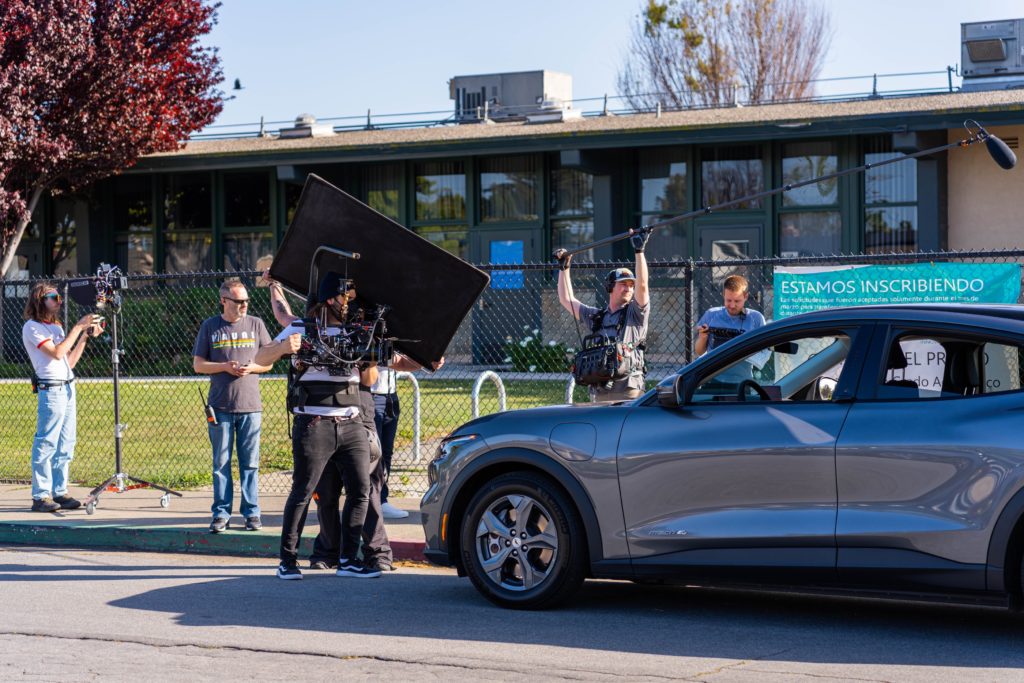
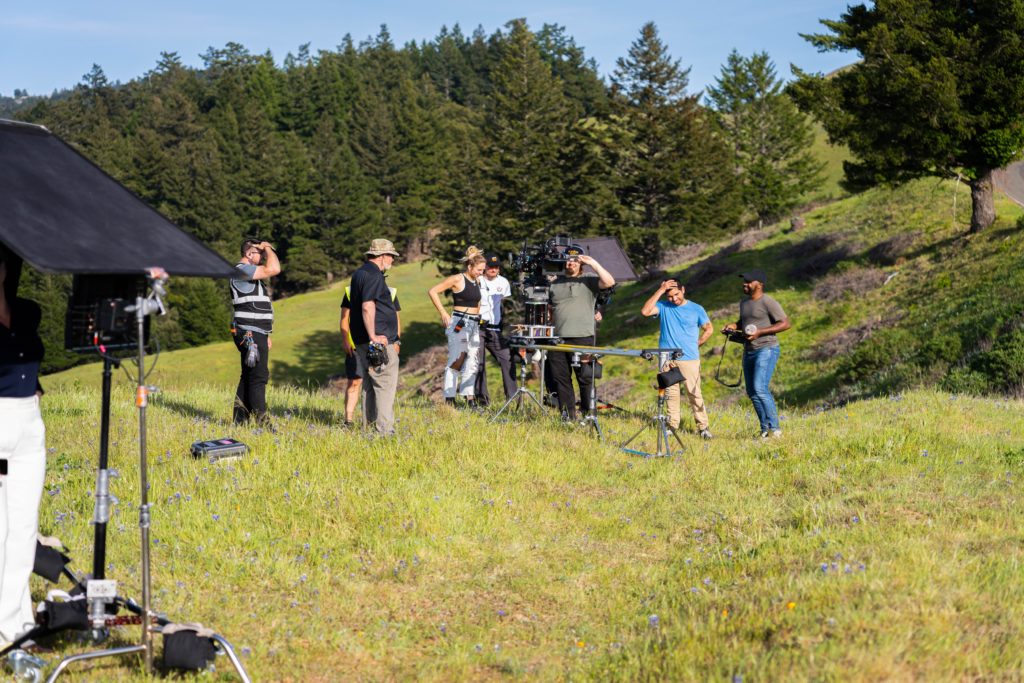
Production
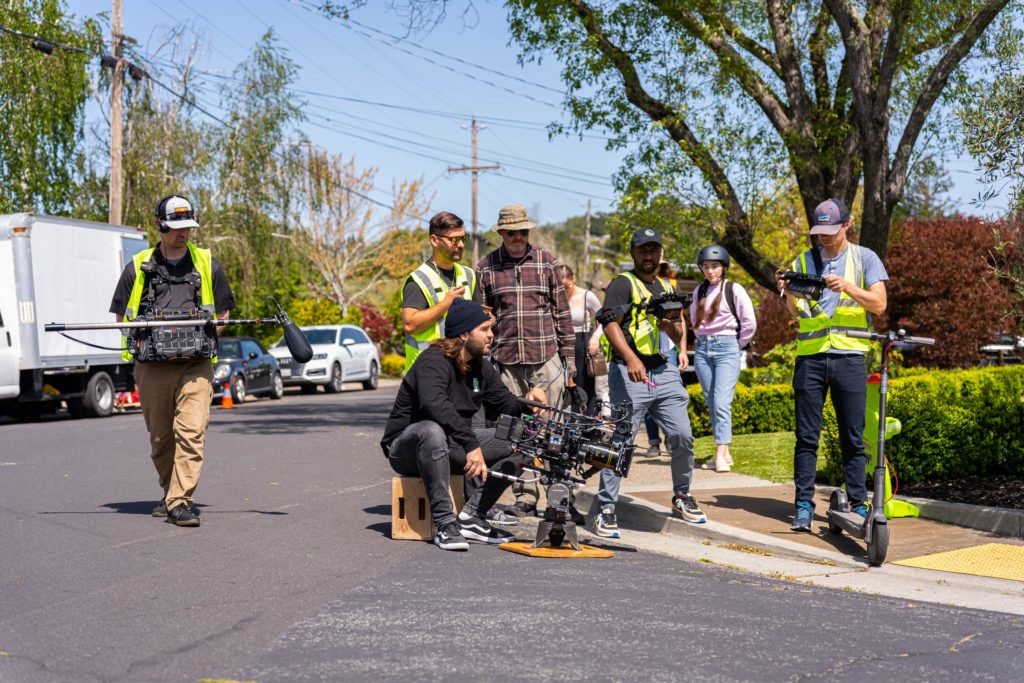
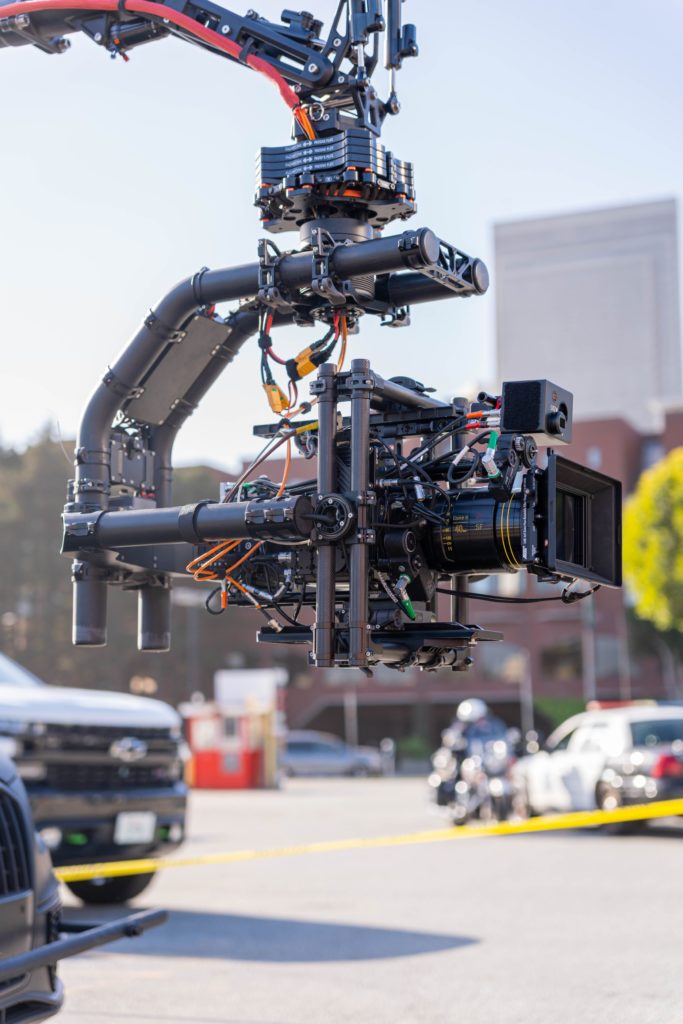
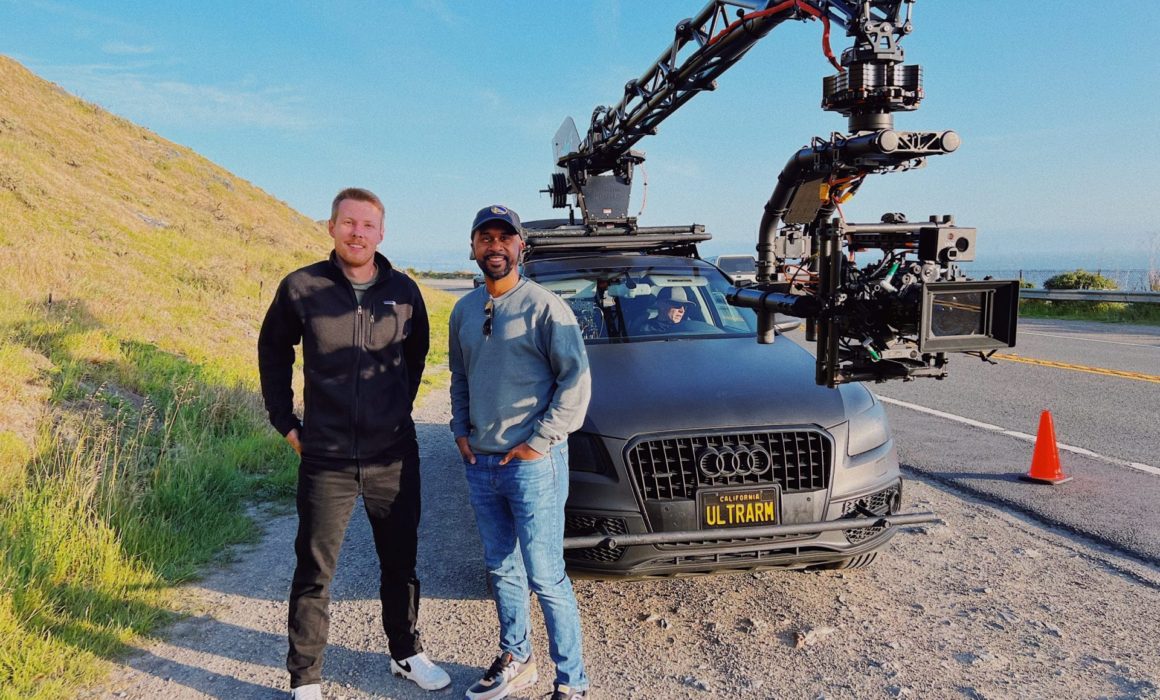
Once we completed the pre-production phase it was time for some fun! The four shoot days involved approximately twenty crew and each one of them was necessary to make sure we are able to not only get the cinematic shots that would represent their brand well, but would also keep us safe on the road. For day one, the russian arm day, where we were doing all of our shots on the road, we hired the local arm car company as well as San Francisco police and California highway patrol(CHP). This meant we would have full access to the road! It also helped that our locations manager was good friends with the SF film commission.
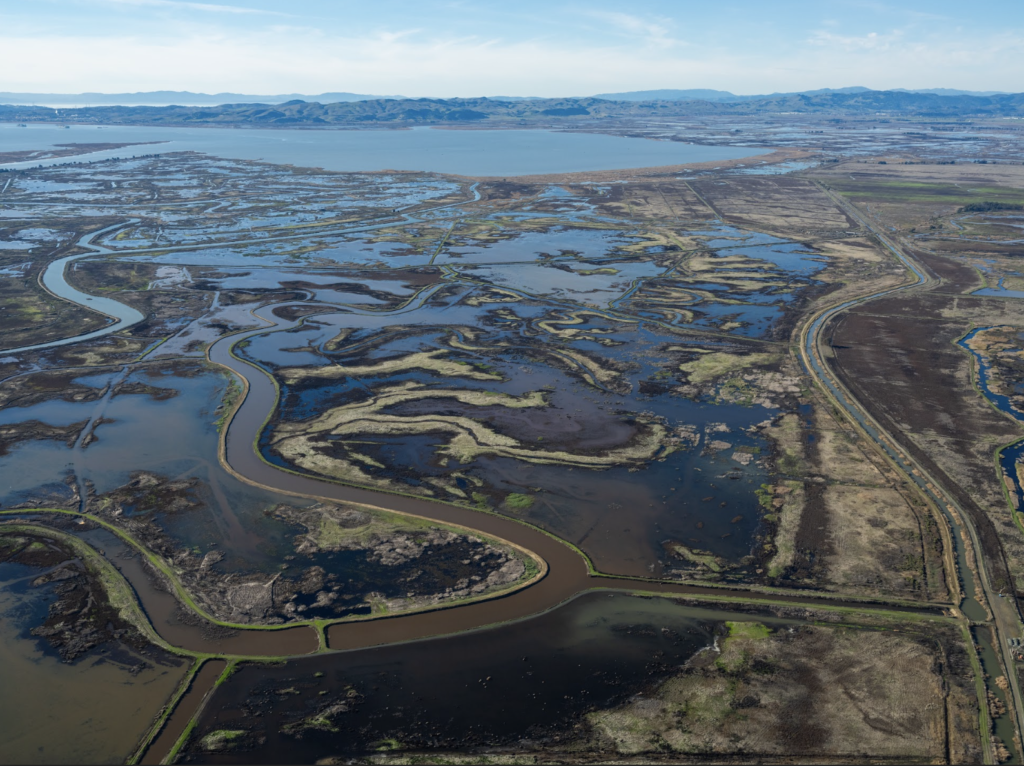
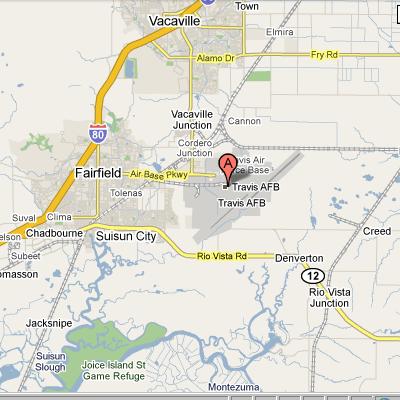
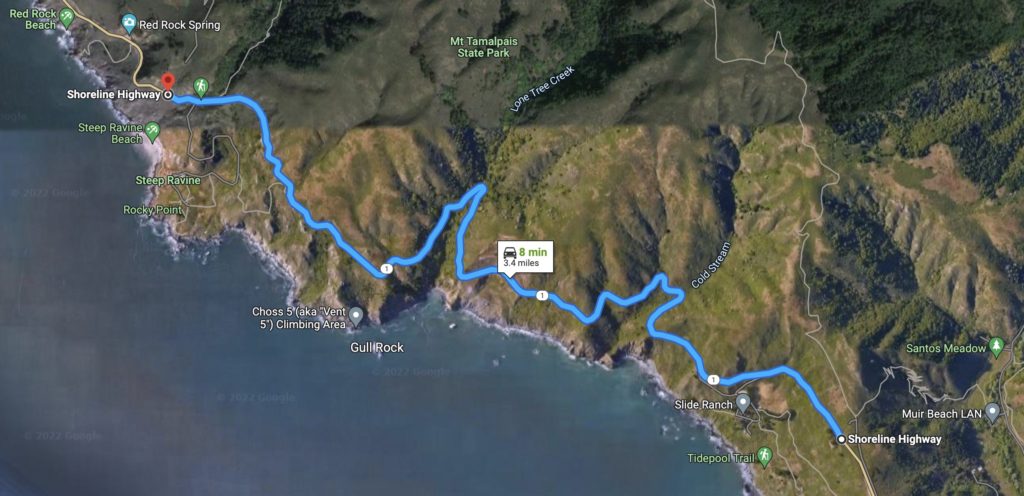
It was our first time being able to completely stop traffic and it was quite exhilarating. In the morning, we shot in downtown San Francisco by the Embarcadero as well as in the financial district. In the afternoon we went over the Marin and did our neighborhood driving shots as well as the coastal shots. This part of the day involved the CHP shutting down highway one between for a stretch of road between Muir beach and Stinson beach.
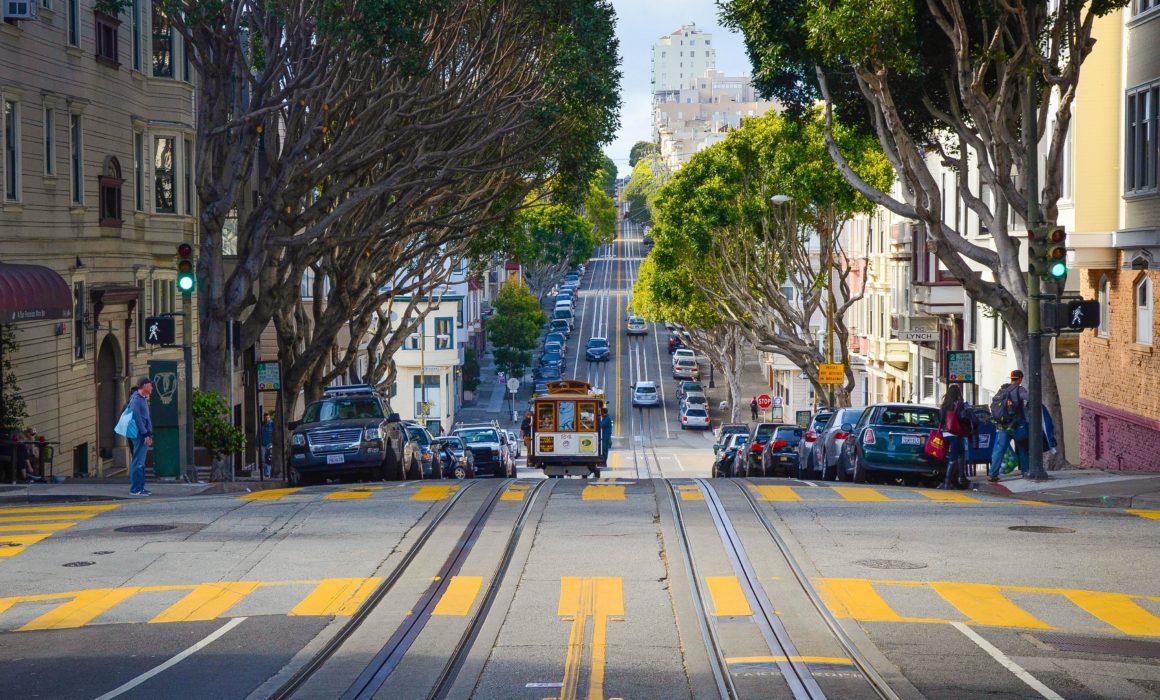
The image below shows the stretch of road on highway where the CHP shut down the road so we could film safely.

After we finished day one, we knew the shoot was going to be relatively smooth sailing. Day two involved our team shooting in the South Bay for the R&D scenes at their headquarters in San Jose. In the afternoon, we shot at a nearby house and school to get the daughter departure scene as well as the arrival. Because it was mandatory that we filmed at their headquarters in the South Bay, it only made sense that we shot the house and school in the South Bay as well.
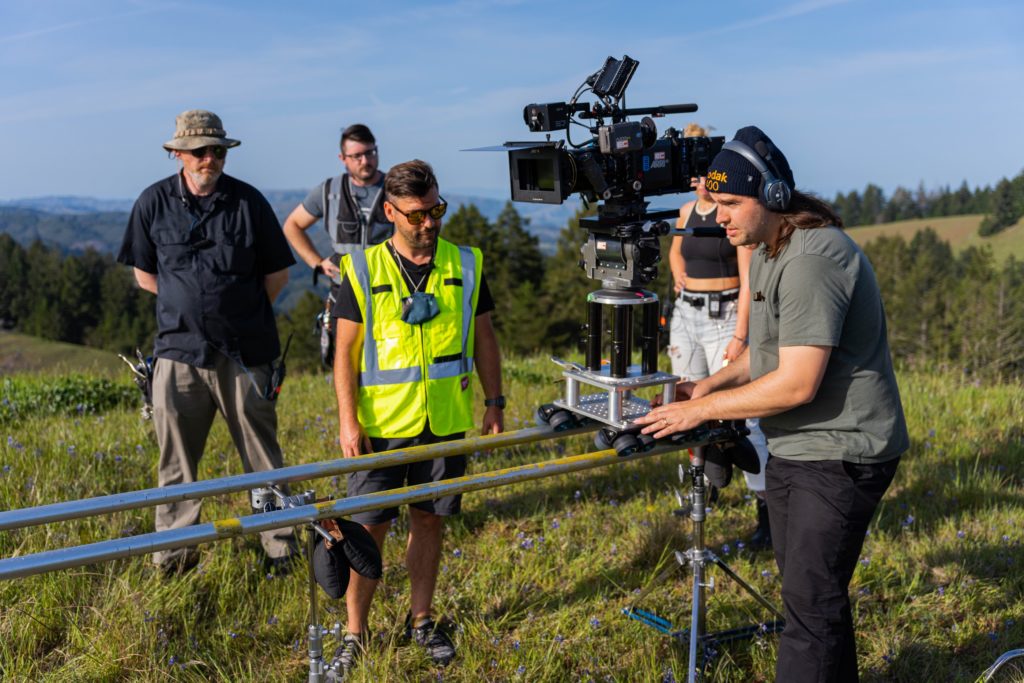
On day three we were in Marin for the kids departure scene as well as the near accident scene and the coastal driving in car shots. These location moves were tricky, with trying to move so many crew but we got it done!
For day four we were in San Francisco for the couple departure scene as well as the in car city shots and the business woman arrival. We finished up the shots up at Mount Tamalpais for the kids arrival scene. We definitely scored on the weather!
Quick behind the scenes video from the shoot.
Post Production
Once we captured all the footage from the shoot, it was just a matter of assembling things to get post production started! Our editor put together an assembly cut within a week and we were loving what we were seeing. Because their technology is inherently visual with how it uses lasers to map out the world around it, we knew VFX was going to take some time. We began sharing the plates of the scenes that would need visual effects integration with our VFX team. With regards to the GIF below, we took the drone shot of the truck on the road and then sent this to our VFX artist who then recreated the real world in a virtual setting by using a model of the same truck and animating it to show the distance that their lidar technology could detect.

The client was particular about how their technology was portrayed on screen so we spent extra time making sure their lidar technology was portrayed correctly on screen.

Once the client had signed off on the VFX, we were able to picture lock the video. At this stage, we moved on to color correction and sound design to put the finishing touches on the video.
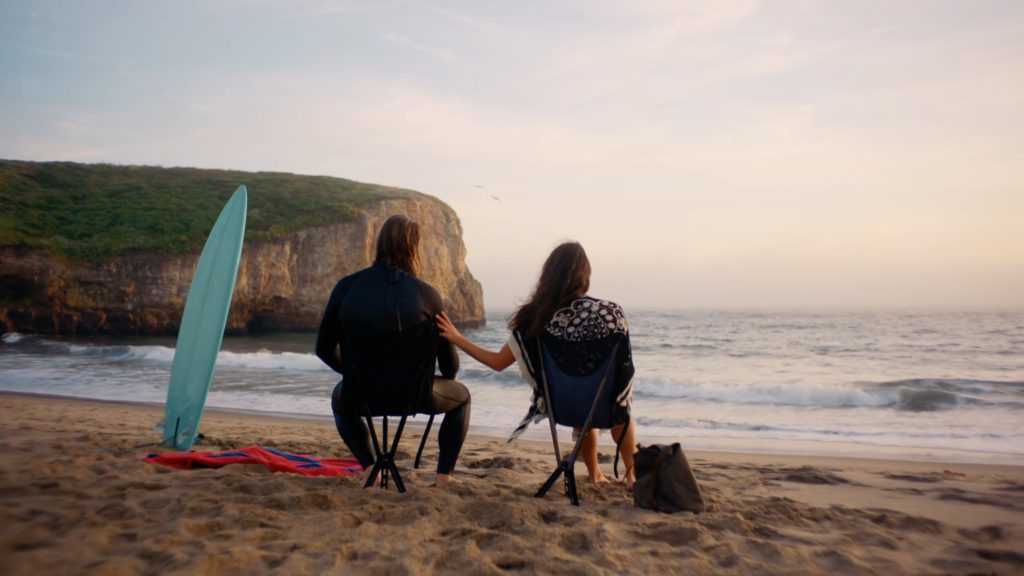
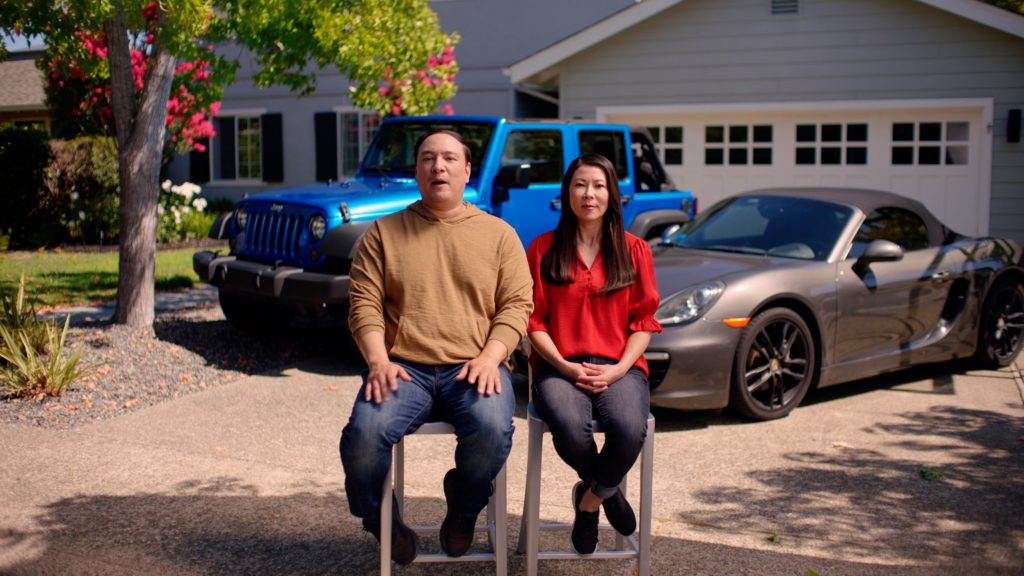
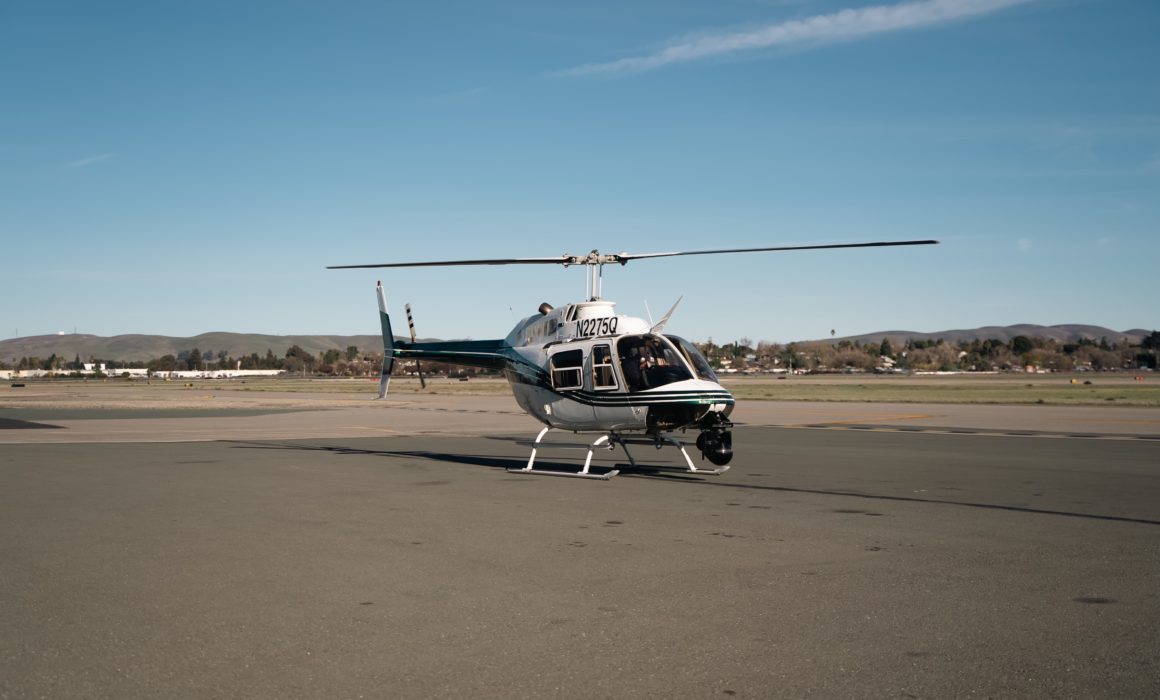
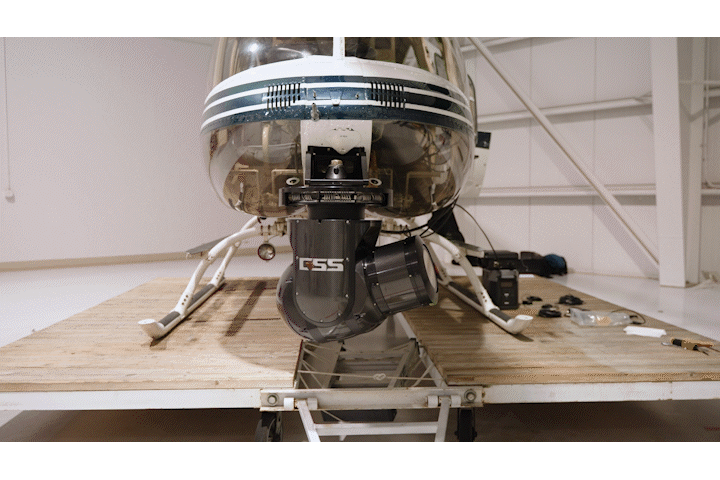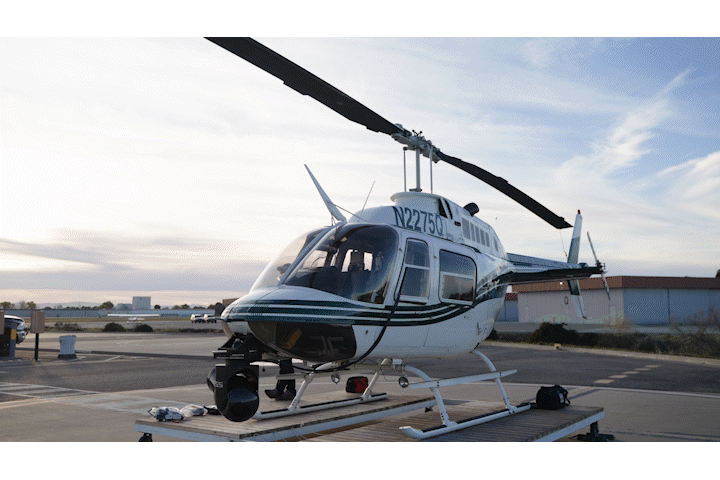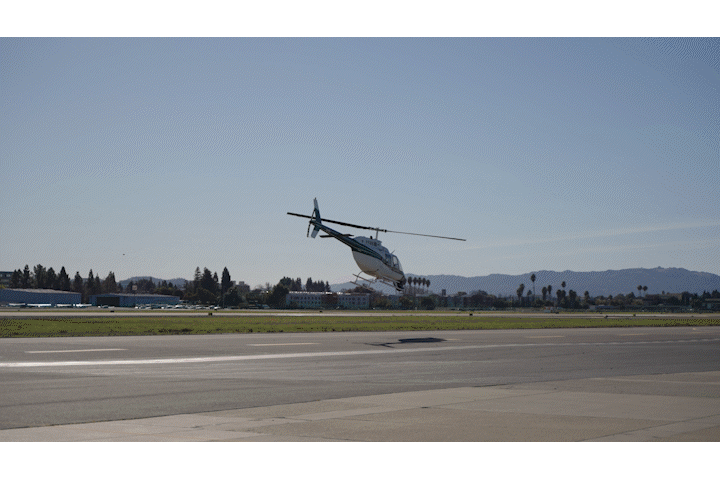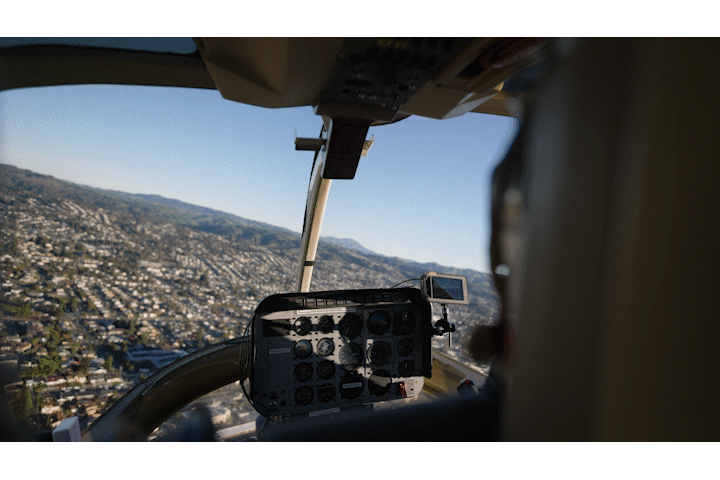
BTS Photos
Conclusion
We had a ton of fun on this production. It was our largest San Francisco brand video production so far. And it was also the project that our team put the most amount of hours into. As we continue to evolve as a company, it’s this type of work that we’d like to continue getting the opportunity to create! If you or your company are looking for a cinematic professional brand video, contract us today!